
Vaidyanathan Hariharan
- July 20, 2021
- 0

E0 Plywood & Boards Standards & Practices (Part 1)
As the world is shifting quickly to concepts of sustainability, low emission, environmental concerns etc., the plywood and panel sector too is gearing up to ensure Low Formaldehyde Emission (LFE) resins & boards. Therefore, it is very important to be aware precisely, the different formaldehyde emission standards prescribed worldwide.
What is E0?
E0 refers to the European way of talking about LFE boards. Each standard prescribes certain upper limits of formaldehyde emission values from manufactured boards that can be sold in the respective markets where the particular standard holds jurisdiction.
For example: To sell plywood/PB/MDF in California, a manufacturer will have to abide by the ARB (Air Resources Board) norms, popularly known as the CARB Phase1 & Phase2 formaldehyde emission standards.
E0 प्लाईवुड और बोर्ड मानक और व्यवहार (भाग 1)
जैसा कि दुनिया तेजी से स्थिरता, कम उत्सर्जन, पर्यावरण संबंधी चिंताओं आदि की अवधारणाओं की ओर बढ़ रही है, प्लाईवुड और पैनल क्षेत्र भी कम फॉर्मलाडेहाइड उत्सर्जन (एलएफई) रेजिन और बोर्ड सुनिश्चित करने के लिए कमर कस रहे हैं। इसलिए, दुनिया भर में निर्धारित विभिन्न फॉर्मलाडेहाइड उत्सर्जन मानकों के बारे में सटीक रूप से अवगत होना बहुत महत्वपूर्ण है।
E0 क्या है?
E0 LFE बोर्डों के बारे में बात करने के यूरोपीय तरीके को संदर्भित करता है। प्रत्येक मानक विनिर्मित बोर्डों से फॉर्मलाडेहाइड उत्सर्जन मूल्यों की कुछ ऊपरी सीमाएं निर्धारित करता है जिन्हें संबंधित बाजारों में बेचा जा सकता है जहां विशेष मानक अधिकार क्षेत्र रखता है।
उदाहरण के लिए: कैलिफ़ोर्निया में प्लाईवुड/पीबी/ एमडीएफ बेचने के लिए, एक निर्माता को एआरबी (वायु संसाधन बोर्ड) मानदंडों का पालन करना होगा, जिन्हें लोकप्रिय रूप से सीआरबी चरण 1 और चरण 2 फॉर्मलाडेहाइड उत्सर्जन मानकों के रूप में जाना जाता है।
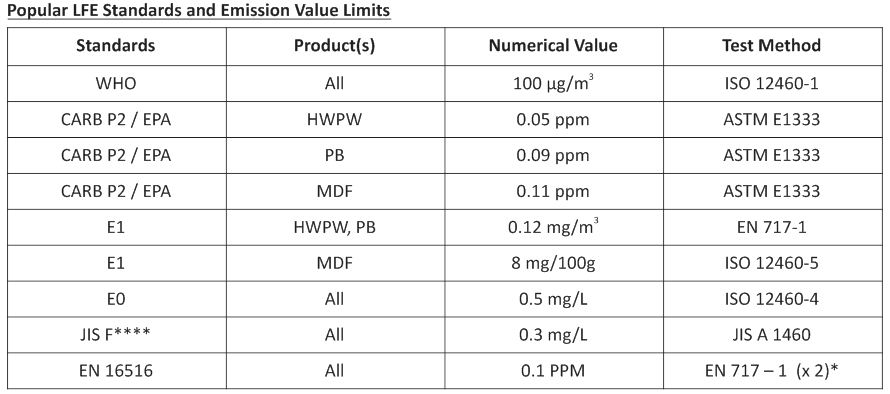
* – New harmonised European Standard limits = EN 717 Large Chamber value multiplied by factor 2
Similarly, there are also country-wise LFE standards such as BS, AS/NZS, GB/T, DIN and so on. But, the above values are most commonly followed worldwide, unless specifically stated otherwise.
-
- ASTM – American Society for Testing Materials,
- ISO – International Standards Organisation
- EN – European Standards
- JIS – Japanese Industrial Standards
- CARB P2 – California Air Resources Board Phase 2
- EPA – (US) Environment Protection Agency
- AS/NZS – Australia / New Zealand Standards
- GB/T – Guobiao Standards / Tuījiàn – Chinese Standards
- DIN – Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V. (German Institute for Standardisation)
- HWPW – Hard Wood Ply Wood
- LFE – Low Formaldehyde Emission
- BS – British Standards
Popular Tests for Determination of Formaldehyde Release
ISO 12460 – 1: Large Chamber EN 717 – 1: Chamber Method
ISO 12460 – 2: Small Chamber EN 717 – 2: Gas Analysis
ISO 12460 – 3: Gas Analysis EN 717 – 3: Flask Method
ISO 12460 – 4: Desiccator ASTM E 1333: Large Chamber
ISO 12460 – 5: Perforator ASTM D 6007: Small Chamber
JIS A 1460: Desiccator ASTM D 5582: Desiccator
Why different tests have different measurement units?
Japanese F**** (pronounced as F – four star) is the most stringent level of formaldehyde emission with average value of less than or equal to 0.3 mg/L. The so-called zero formaldehyde emission is defined as ≤ 0.3 mg/L, because the formaldehyde emission from natural wood has generally been found to be 0.1 to 0.3 mg/L, tested by the desiccator method.
The unit and value of formaldehyde limit indicators are different, due to different testing methods.
mg/100g – refers to the formaldehyde “content” per 100g oven dry wood-based panels – perforator method.
mg/L – corresponds to formaldehyde “emission” in the desiccator method, which is related to temperature, specimen area, dry air volume, water volume, and collection time. [µg/mL – American desicccator measurement unit]
mg/m3 ; PPM ; µg/m3 – corresponds to formaldehyde “emission” in chamber method, related to humidity, temperature, air loading rate, ventilation, sampling port, sample size, sampling time, and analysis methods.
mg/m2.h – corresponds to formaldehyde “emission” in gas analysis method, using the measured concentration of formaldehyde, extraction time, and exposed area of specimen.
Which is the best universal test for Internal Quality Control?
The best internal (factory) laboratory quality control testing mechanism is the Japanese Desiccator test – JIS A 1460.
Reason: JIS A 1460 desiccator method is approved by CARB & EPA (USA) for formaldehyde emission testing of all wood based panel & composite products. Notifications in this regard may be downloaded for reference from https://ww2.arb.ca.gov/resources/documents/formaldehyde-composite-wood-products-test-methods. JIS A 1460 desiccator method is also harmonised with European formaldehyde emission standards, and is a worldwide approved quality control test method, in general, valid for all composite panel products.
[Next issue – Part 2: Details of formaldehyde emission from composite products, difference between ‘content’ & ’emission’, reasons…]
https://www.linkedin.com/in/krdf
krdfindia@outlook.com




