
Effects of core veneer thickness variation in plywood
- नवम्बर 14, 2022
- 0

Dr. S K Nath Ex Joint Director IPIRTI
Author
Plywood Manufacturing Practices in Indian Industry
(Only book by an Indian Author)
What happens if :
1. There is thickness mismatch variation of veneer in construction in making plywood? For example, half of a layer is of 2.5mm and the other half is of 1.8mm or less.
2. Mixing of various species of timber in a piece of plywood – irrespective of segregation of hard and soft wood?
3. Separate layer of soft and hard wood veneer are used in a single piece of plywood?
Plywood is a layered panel made by assembling veneer one above another and bonding layer to layer by adhesive by application of pressure at room / elevated temperature. Formation of bond requires that the two surfaces of veneer come in close contact to each other with adhesive in between while under pressure.
 If in one layer of veneer, there is thickness variation, the veneer having higher thickness will come in contact with the surface of veneer in the opposite layer when pressure is applied and will get bonded as the resin cures. But the veneer having lower thickness will not get adequate contact with the veneer in opposite layer and on curing of resin, bond in those areas will be poor or even no bond. Thickness variation up to 5% between two individual veneer can be tolerated, beyond which bonding may get affected.
If in one layer of veneer, there is thickness variation, the veneer having higher thickness will come in contact with the surface of veneer in the opposite layer when pressure is applied and will get bonded as the resin cures. But the veneer having lower thickness will not get adequate contact with the veneer in opposite layer and on curing of resin, bond in those areas will be poor or even no bond. Thickness variation up to 5% between two individual veneer can be tolerated, beyond which bonding may get affected.
Similar is the case with use of veneer of mixed species having different densities. Under pressure veneer will compress, but the compression will vary depending on the density of veneer – low density veneer will be compressed more than high density veneer under the same pressure. Proximity of contact with the veneer of opposite layer will consequently vary and hence the bonding. Secondly, with assorted distribution of veneer of low and high density, there will be non-uniform densities in the same panel which will ultimately tend to warp.
Remedial Measures:
1. Segregation of logs of different species before peeling and peel them separately.
2. Segregation of green veneer as per thickness and species after peeling.
3. Maintain separate heap as per thickness and species after drying.
4. Practice pre-assembly of veneer before gluing and assembling. Veneer of only one species and one thickness should be used for composing one glue core layer and panel layer.
5. Supply pre-composed veneer layer of glue core and panel to glue spreader as per the composition of plywood of a particular thickness.
6. Plywood composition should be balanced w.r.t. veneer thickness and species on either side from centre of composition of any plywood thickness.
Example: 19mm plywood.
Veneer composition:
Face/gc(1)/p(2)/gc(3)/p(4)/gc(5)/p(6)/gc(7)/p(8)/gc(9)/p(10)/gc(11)/Face
gc = glue core, p = panel
Option for veneer layer:
1. All layers are of same thickness and one species.
2. In the above construction, layer p(6) is the centre of composition.
3. i. If any variation of thickness or species of veneer in any layer has to be made, it should be done in two opposite layers equidistant from the central layer e.g., 1 and 11, 4 and 8 etc.
ii. No single layer can be of different thickness or species except the central layer, p(6).
iii. However, when veneer of different thickness and/ or species are used, both the layers must be of the same thickness and one species only.
क्या होगा यदि :
1. प्लाईवुड बनाने में कोर विनियर की मोटाई बेमेल है? उदाहरण के लिए, एक परत का आधा हिस्सा 2.5 मिमी का होता है और दूसरा आधा 1.8 मिमी या कम का होता है।
2. प्लाईवुड की परत टुकड़े में लकड़ी की विभिन्न प्रजातियों का मिश्रण – कठोर और मुलायम लकड़ी का एक साथ प्रयोग करना?
3. प्लाईवुड के नरम और कठोर लकड़ी की अलग-अलग परत का उपयोग किया जाना
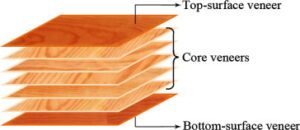 प्लाइवुड एक स्तरित पैनल है जो विनियर को एक दूसरे के ऊपर असेंबल करके और कमरे/उच्च तापमान पर दबाव के अनुप्रयोग द्वारा एडहेसिव द्वारा परत दर परत बॉन्डिंग द्वारा बनाया जाता है। बंधन के निर्माण के लिए आवश्यक है कि विनियर की दो सतहें दबाव में रहते हुए बीच-बीच में चिपकने के साथ एक-दूसरे के निकट संपर्क में आएं।
प्लाइवुड एक स्तरित पैनल है जो विनियर को एक दूसरे के ऊपर असेंबल करके और कमरे/उच्च तापमान पर दबाव के अनुप्रयोग द्वारा एडहेसिव द्वारा परत दर परत बॉन्डिंग द्वारा बनाया जाता है। बंधन के निर्माण के लिए आवश्यक है कि विनियर की दो सतहें दबाव में रहते हुए बीच-बीच में चिपकने के साथ एक-दूसरे के निकट संपर्क में आएं।
यदि विनियर की एक ही परत में, मोटाई भिन्नता होती है, तो उच्च मोटाई वाला विनियर दबाव डालने पर विपरीत परत में विनियर की सतह के संपर्क में आ जाएगा और रेजीन के प्रभाव से बंध जाएगा। लेकिन कम मोटाई वाले विनियर को विपरीत परत में विनियर और रेजीन के साथ पर्याप्त संपर्क नहीं मिलेगा और उन क्षेत्रों में बंधन कम होगा या कोई भी बंधन नहीं होगा। दो अलग-अलग विनियर की परतों कि बीच 5 प्रतिशत तक मोटाई भिन्नता को सहन किया जा सकता है, जिसके आगे बॉन्डिंग प्रभावित हो सकती है।
विभिन्न घनत्वों वाली मिश्रित प्रजातियों के विनियर के उपयोग के मामले में भी ऐसा ही है। दबाव के तहत विनियर संपीड़ित होगा, लेकिन विनियर के घनत्व के आधार पर संपीड़न अलग-अलग होगा – कम घनत्व वाले विनियर को उसी दबाव में उच्च घनत्व वाले विनियर से अधिक संकुचित होंगे। परिणामतः विपरीत परत के विनियर के साथ संपर्क की निकटता भिन्न होगी और इसलिए बंधन। दूसरे, कम और उच्च घनत्व के विनियर के मिश्रित वितरण के साथ, एक ही पैनल में गैर-समान घनत्व होंगे जिसे पेनल घुमाव पर हो जाएंगे, सीधपन खो देंगे।
उपचारी उपाय:
1. विभिन्न प्रजातियों के लट्ठों को छीलने से पहले अलग कर लें और उन्हें अलग-अलग छील लें।
2. छीलने के बाद मोटाई और प्रजातियों के अनुसार कच्चे विनियर का पृथक्करण।
3. सुखाने के बाद मोटाई और प्रजाति के अनुसार अलग-अलग ढेर बनाकर रखें।
4. ग्लूइंग और असेंबलिंग से पहले विनियर की प्री-असेंबली का अभ्यास करें। एक ग्लू कोर परत और पैनल परत की रचना के लिए केवल एक प्रजाति और एक मोटाई के विनियर का उपयोग किया जाना चाहिए।
5. एक विशेष मोटाई के प्लाईवुड की संरचना के अनुसार ग्लू कोर और पैनल की पूर्व-निर्मित विनियर को ग्लू स्प्रेडर में आपूर्ति करें।
6. प्लाइवुड की संरचना संतुलित होनी चाहिए किसी भी प्लाईवुड की मोटाई की संरचना के केंद्र से दोनों तरफ विनियर की मोटाई और प्रजातियां।
उदाहरण : 19 मिमी प्लाईवुड।
विनियर संरचना
फेस/जीसी(1)/पी(2)/जीसी(3)/पी(4)/जीसी(5)/पी(6)/जीसी(7)/पी(8)/जीसी(9)/ पी(10)/जीसी(11)/फेस
जीसी = ग्लू कोर, पी = पैनल
विनियर परत के लिए विकल्प :
1. सभी परतें समान मोटाई और एक प्रजाति की होती हैं।
2. उपरोक्त निर्माण में, परत च(6) रचना का केंद्र है।
3. i ) यदि किसी परत में मोटाई या विनियर की प्रजातियों में कोई परिवर्तन करना हो, तो इसे केंद्रीय परत से समान दूरी पर दो विपरीत परतों में किया जाना चाहिए जैसे, 1 और 11, 4 और 8 आदि।
ii) केंद्रीय परत को छोडकर कोई भी परत विभिन्न मोटाई या प्रजातियां नहीं हो सकती है, पी(6)।
iii) हालांकि, जब विभिन्न मोटाई और/या प्रजातियों के लिबास का उपयोग किया जाता है, तो दोनों परतें एक ही मोटाई और केवल एक प्रजाति की होनी चाहिए।




Ply insight launched on March 2018 with a vision to make a platform to collaborate plywood MDF, Laminate, machinery manufactures with dealers in the Trade.
Categories
Useful Links
Follow Us