
Vaidyanathan Hariharan – E0 Plywood & Boards – Standards & Practices (Part 6)
- December 30, 2021
- 0

E0 Plywood & Boards – Standards & Practices (Part 6)
Test Procedure & Calculations (contd.)
Test procedure for JIS A-1460 desiccator consists of following steps:
I. Stabilising 2 set of test samples by conditioning to a consistent mass.
ii. Making & standardising formaldehyde stock solution.
iii. Using standardised formaldehyde stock dilutions for making calibration curve.
iv. Spectrophotometer reading and making the calibration curve.
v. Standardising Sodium Thiosulphate solution.
vi. Making fresh reagents for reaction procedures.
vii. 24 hour desiccator procedure for – blank, sample set 1, sample set 2.
viii. Spectrophotometer readings and calculations.
v. Standardising Sodium Thiosulphate solution.
Accurately weigh 210mg of Potassium Dichromate, previously pulverised and dried at 120 deg C for 4 hours. Dissolve in 100ml distilled water, in a glass stoppered 500mL conical flask.Remove the stopper, and quickly add 3g Potassium Iodide, 2g of Sodium Bicarbonate, and 5mL Hydrochloric Acid. Insert stopper and swirl gently to mix. Allow to stand exactly for 10 minutes. Rinse stopper & inner walls of flask with distilled water and titrate liberated Iodine with the Sodium Thiosulphate solution until solution turns yellowish green colour. Add 3mL starch indicator solution & continue titration until blue colour is discharged. Perform blank test. Molarity of Sod. Thiosulphate = Wt of Pot Dichromate (mg) / (49.04 X Sod Thiosuphate in mL).

v. Making fresh reagents for reaction procedures.
- Iodine solution (0.05 mol/L): 40g of Potassium Iodide dissolved in 25mL of D water, 13g of Iodine is dissolved in it, & transferred to 1000mL vol. Flask. 3 drops of hydrochloric acid are added & water made up to marked line. [Ready to mark up solution available in lab reagents]
- Sodium Thiosulphate (0.1 mol/L): 26g of sodium thiosulphate pentahydrate and 0.2g of sodium carbonate are dissolved in 1000mL of water free from dissolved oxygen. Mixture is allowed to stand for 2 days & and standardised. [Ready to mark up solution available]
- Sodium hydroxide solution (1 mol/L): 40g of sodium hydroxide is dissolved in 200mL of water, transferred to a 1000mL vol flask and water added up to the marked line. [Ready solution available]
- Sulphuric acid solution (1 mol/L): 56mL of sulphuric acid is dissolved in 200mL of water, transferred to a 1000mL vol flask & water made up to the marked line. [Ready solution available]
- Starch solution: 1g of soluble starch is thoroughly mixed with 10mL water & added to 200mL of hot water while stirring uniformly. This is boiled for 1 minute, cooled and filtered. Always prepare fresh starch indicator solution.
- Acetyl acetone – ammonium acetate solution: 150g of ammonium acetate is dissolved in 800mL water & 3mL glacial acetic acid & 2mL acetylacetone added to it, mixed thoroughly in solution. Water is added up to marked line of a 1000 mL vol flask. AA solution must always be prepared fresh & can be stored only for a maximum of 3 days at temperature below 10 deg C under refrigeration. It is suggested to prepare one-half the said solution (500mL), to avoid wastage of resources.
v. 24 hour desiccator procedure for – blank, sample set 1, sample set 2.
3 desiccators are required for testing 1 set of samples. 5 set of samples are needed to be tested for one inspection routine. The conditioned test samples of constant mass must be placed inside the desiccators as below:
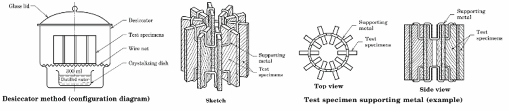
Test atmosphere: The standard testing condition specified is Class 0.5 of JIS Z 8703. Temperature of test condition is 20 ± 0.5 deg C, with RH (65 ± 5)%.
v. Spectrophotometer reading and calculations.
25mL of the test solution from desiccators is taken into a 100mL Erlenmeyer flask. 25mL of acetylacetone-ammonium acetate solution is added and mixed with stopper on. The flask is heated with light mixing in a water-bath at 65±2oC for 10 minutes, and then allowed to stand under shaded condition until it reaches room temperature. This solution is taken into an absorption cell & absorbance is measured at 412 nm wavelength using spectrophotometer. Sometimes, maximum absorbance value is observed at 410 nm. In such a case, all values are taken at this wavelength.
Separately, measurement for the blank test solution should also be carried out the same way.
CALCULATION: Concentration of formaldehyde from test samples, absorbed into water in the glass crystallising dish inside desiccators shall be calculated based on the following formula:
G = F X (Ad – Ab) X 1800 / A
where,
G = concentration of formaldehyde of test solution in desiccators containing sample (mg/L)
Ad = absorbance of test solution in desiccators containing samples
Ab = absorbance of test solution in desiccator for blank test
F = slope of calibration curve of formaldehyde standard solution (mg/L)
A = surface area of test specimen (cm2)
Expression of result: Test result is expressed by the mean value of 2 set of measurements obtained, and the formaldehyde concentration is expressed in mg/L.
[Article Series Concluded]
Vaidyanathan Hariharan (Vaidya) is Founder Director – Kalpaka Research & Development Foundation (KRDF), Ernakulam, Kerala.
KRDF works on product development, process development, standardisation and skill development in manufacturing sectors ranging Sustainability, Biodegradable Single-use Materials, Alternate Natural Material Composites, Coir-Bamboo-Agrowaste Composites, Budget Housing, and Rural technologies.
https://www.linkedin.com/in/krdf ; krdfindia@outlook.com




